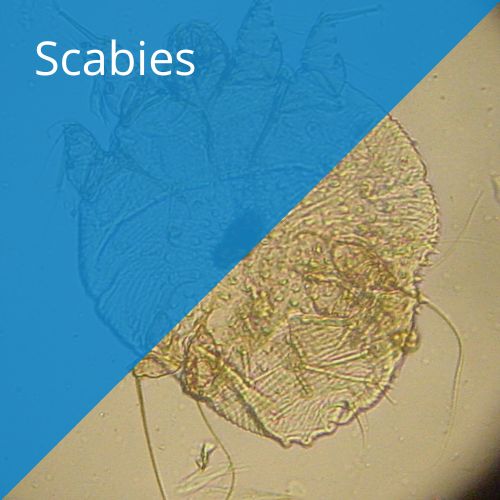
Scabies
Learn more about scabies, symptoms and treatment
Symptoms
How do you know you are suffering from Scabies?
The first time you become infected it will take up to six to eight weeks before itching develops. Intense itching is the most common symptom of scabies. During this time, a couple of generations of scabies mites may have had time to develop. The itching is due to a hypersensitivity reaction in the skin. In people who have had scabies before, the itching develops immediately upon reinfection. Even if no symptoms are observed, infected people are likely to spread Scabies to other individuals. A person becomes a disease carrier immediately upon infection.
After becoming infected, symptoms develop gradually. Itching develops over the first few weeks, though initially people may not take note. After a few weeks of infection, the itching becomes more intense and often disturbs the sleep at night.
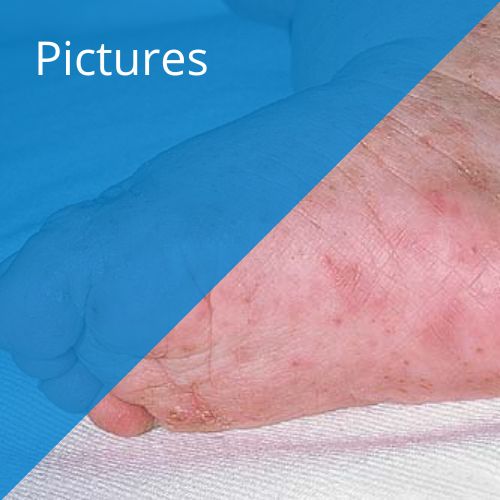
In addition to the intense itching, various skin changes may be seen on the body as a result of vigorous scratching. This may take the form of scratch marks or an eczema-like rash. Small bumps and blisters occur at an early stage. In some individuals, Scabies tunnels may also become visually apparent.
Scabies tunnels are often found on specific areas of the body:
- On the inside of the wrist
- Between fingers
- Elbows
- Around the navel
- Penis and buttocks
- Nipples in women
In infants, it is easiest to detect the mites on the palms or soles of the feet and on the head. It is extremely uncommon to find Scabies on the head of older children and adults.
Scabies, or something else?
Scabies is a condition that is often misdiagnosed. One common reason for this is that the symptoms resemble many other conditions, which may lead to confusion or overlooking Scabies as a possible cause for the symptoms. People are not generally aware that scabies has become increasingly common today, which is another reason that scabies is not always considered as a possible diagnosis.
Scabies symptoms are similar to the following disorders:
Eczema – A chronic skin disease characterized by reddened skin areas, inflammation, blistering and itching. Read more.
Psoriasis – Characterized by irritated red skin areas on the body that itch. Mainly found on knees, abdomen, and elbows. This is also a chronic skin disease. Read more.
Insect bite – May result in skin inflammation, rash and bumps, as well as itching. Read more.
Impetigo – A skin infection caused by bacteria. Symptoms of Impetigo that resemble Scabies include itching, rash and blisters. Read more.
Sidan uppdaterades 2025-06-13
Treatment information
Tenutex® is a cutaneous emulsion containing benzyl benzoate / disulfiram. Tenutex® is a prescription free medicine that is active against Scabies, Head lice, and Pubic lice. Ask your doctor or nurse before using Tenutex® for treating Pubic lice or Scabies. Treatment of Scabies: Wash and dry your body. Carefully massage the hole body except your head with Tenutex®. Only in infants should the head be treated. Wash off thoroughly after 24 hours. In severe infections, repeat the treatment after 1 week. Avoid contact with the eyes. Tenutex® contains cetostearyl alcohol which may cause local skin reactions (e.g. contact dermatitis). Read the patient information leaflet carefully before use.